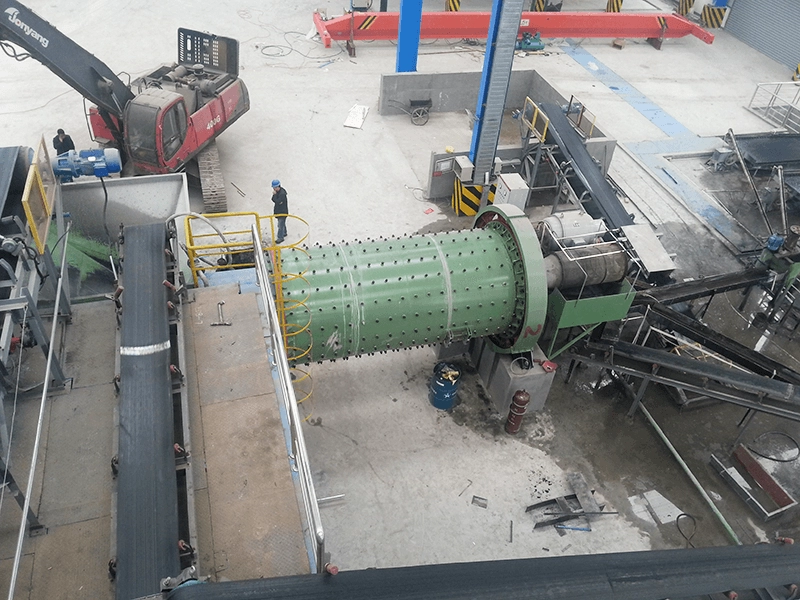
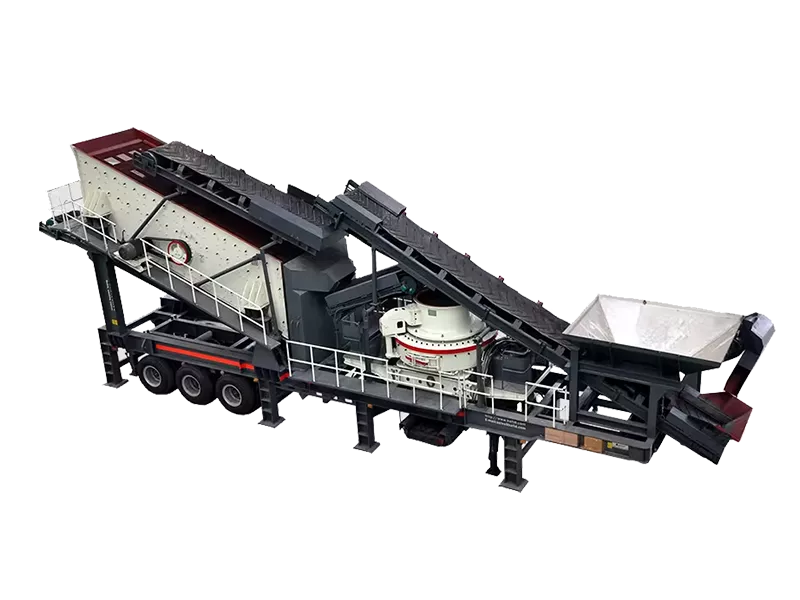
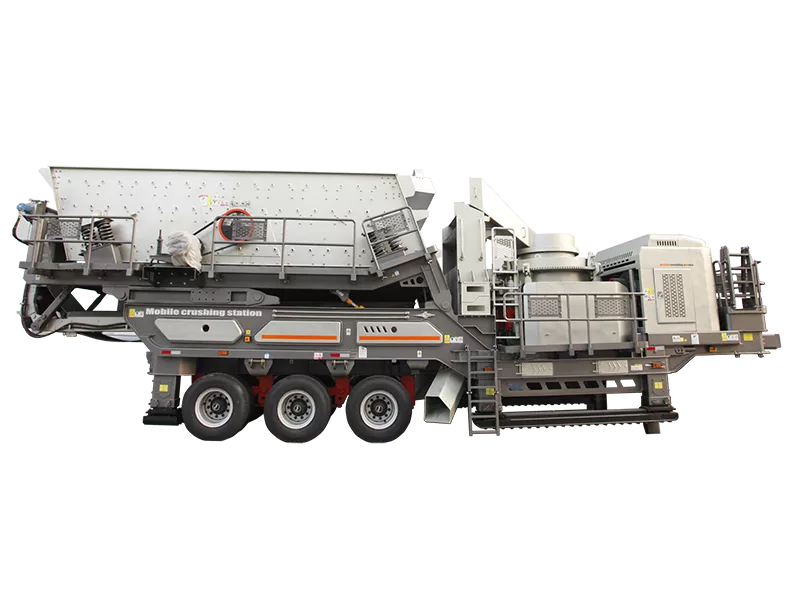
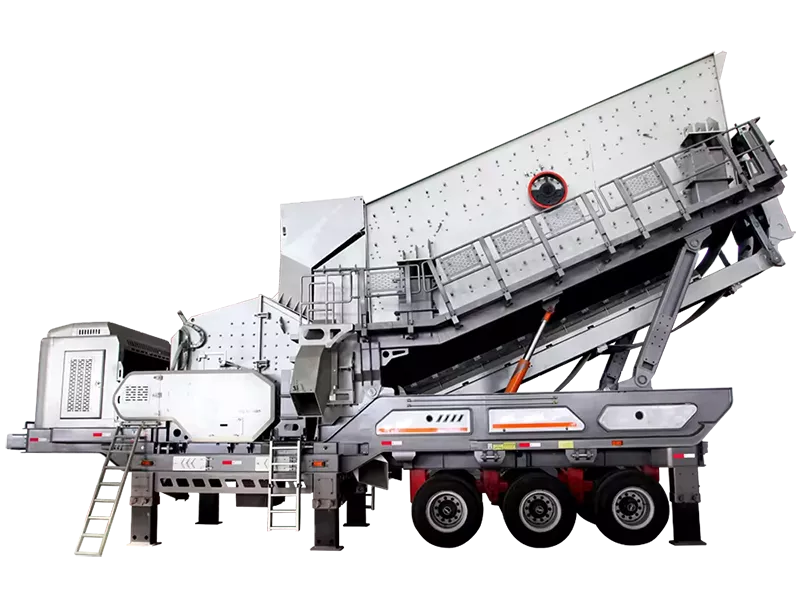
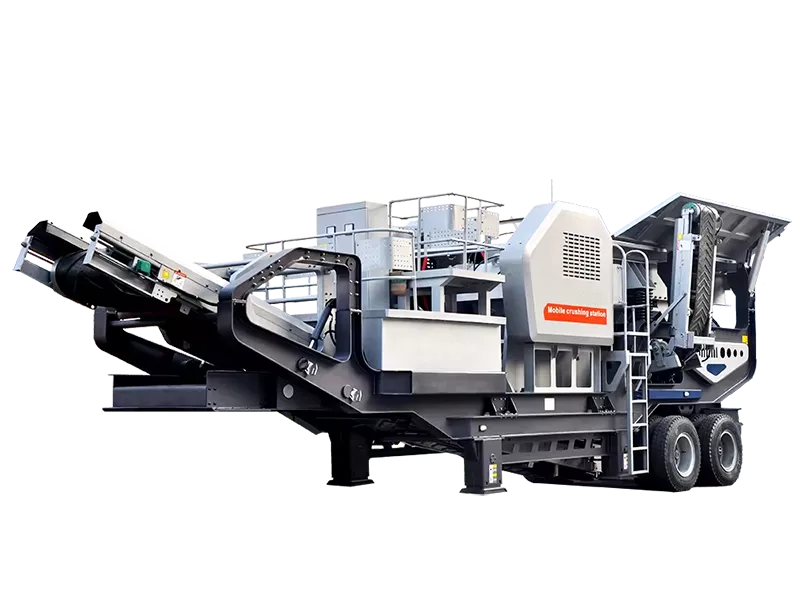
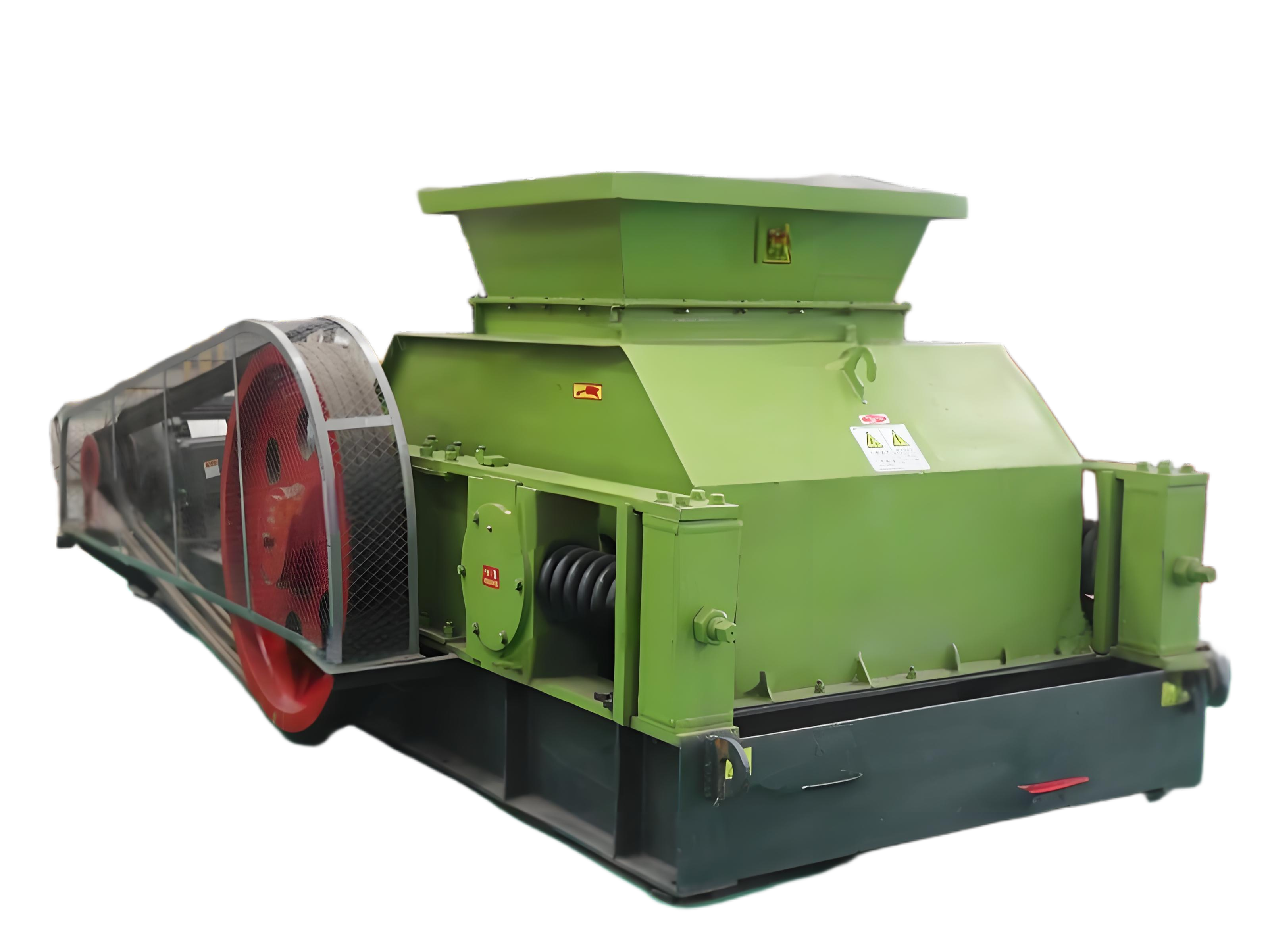
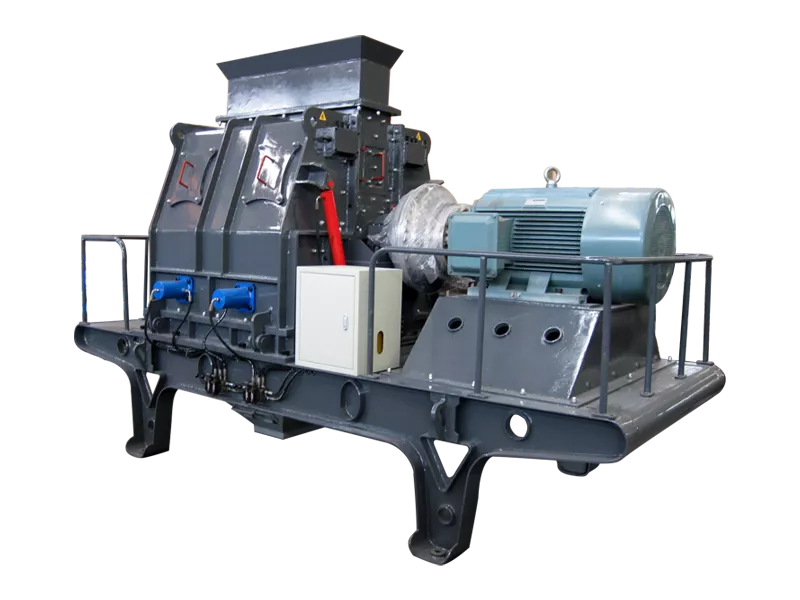
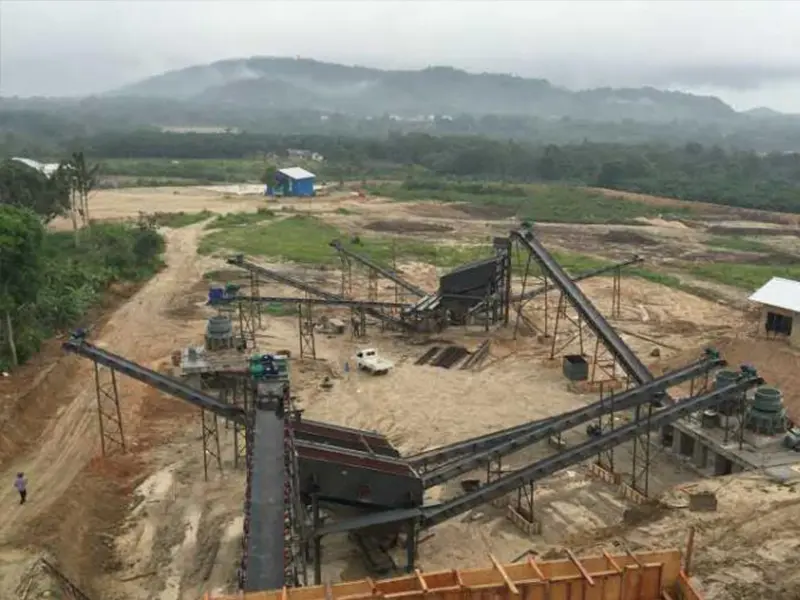
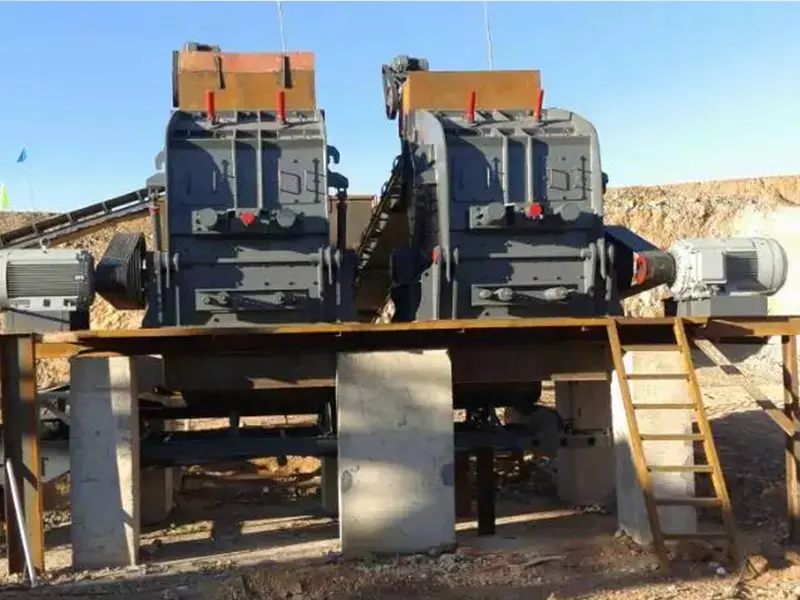
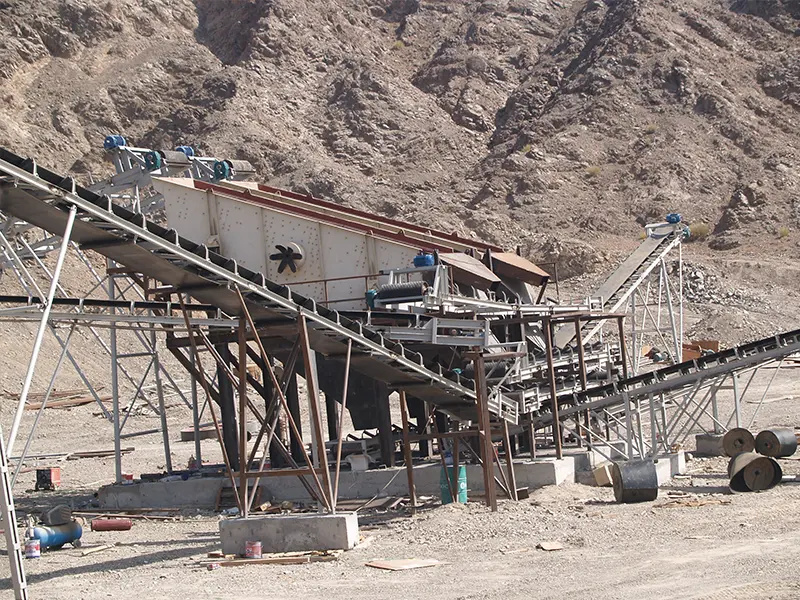
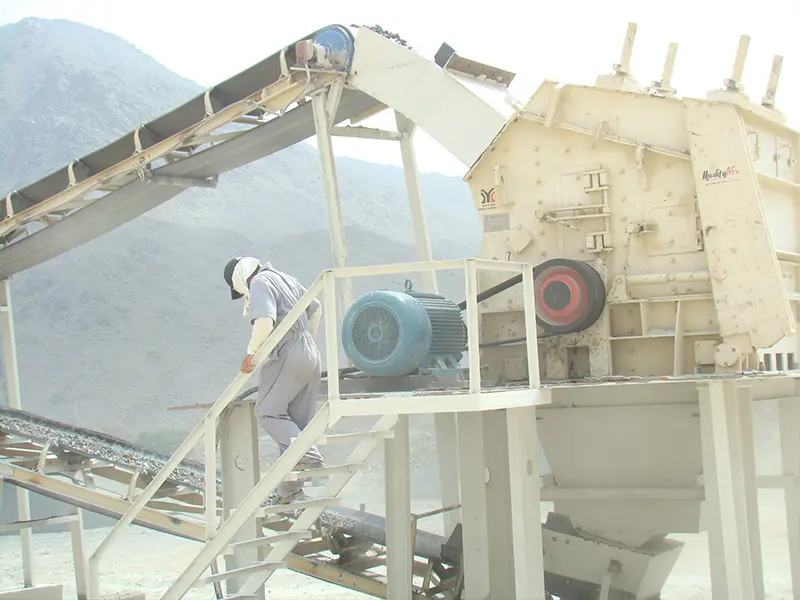
What is the ideal particle size of the discharged material from a ball mill?
2025年5月13日
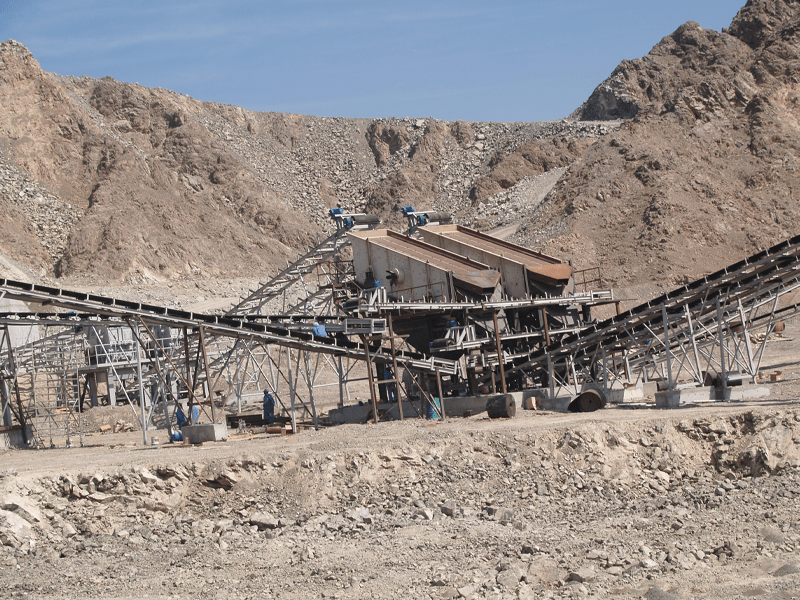
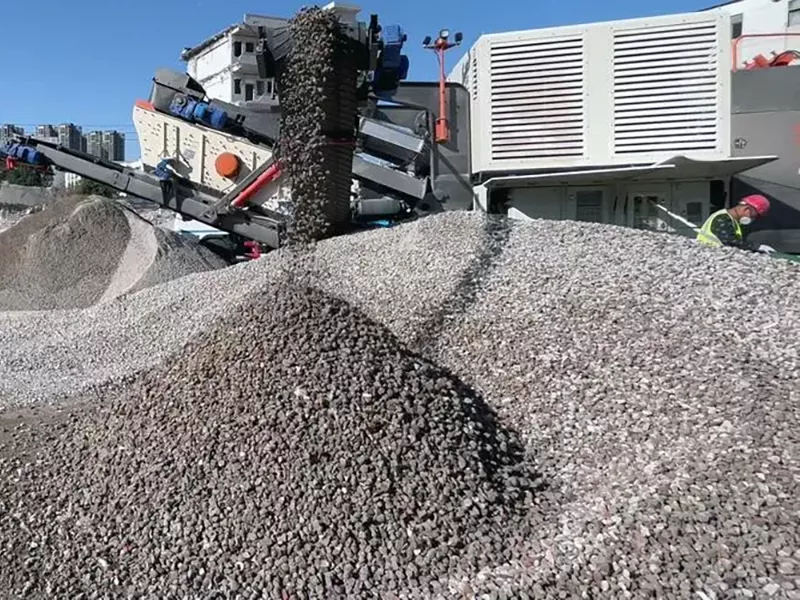
The Problem of Manufactured Sand Loss and Solutions
2025年5月13日
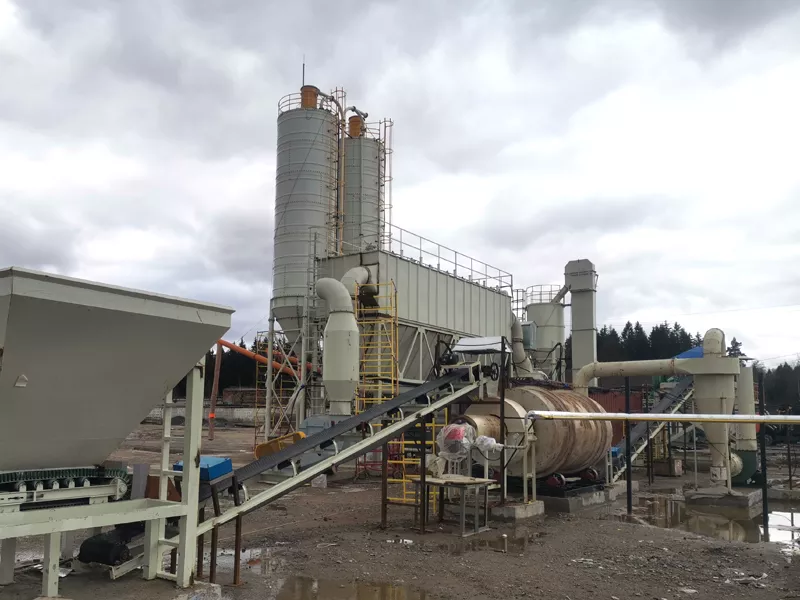
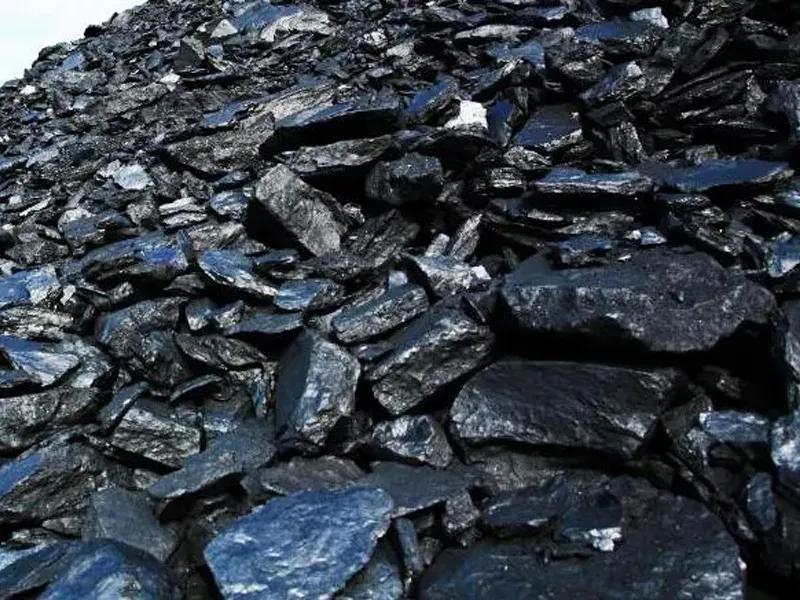
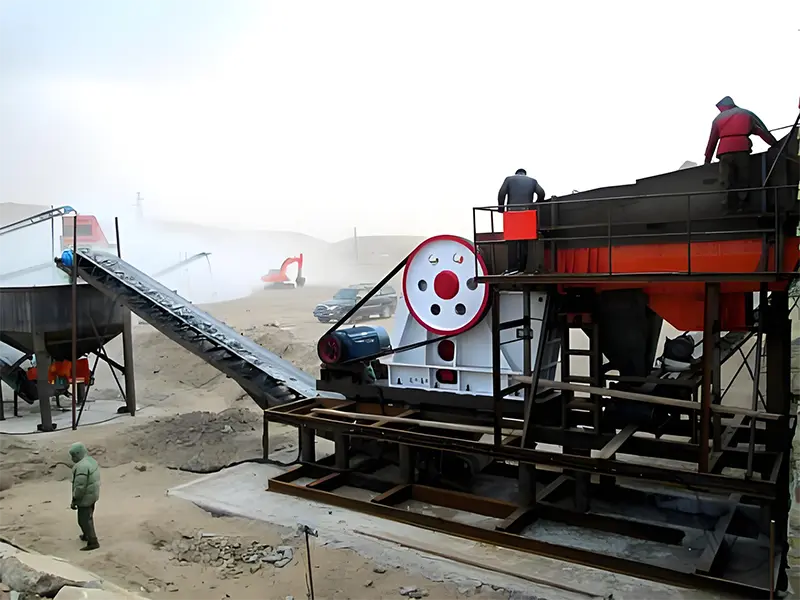
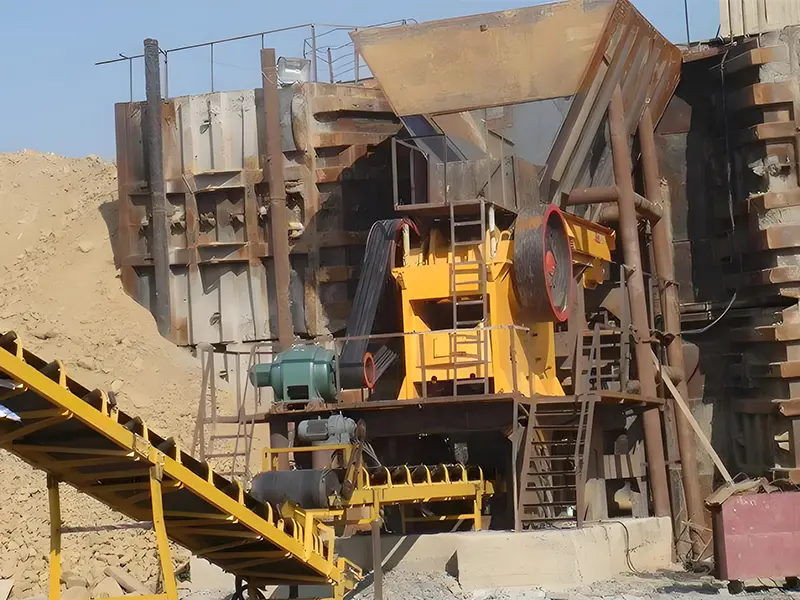
What is the ideal particle size of the discharged material from a ball mill?
2025年5月13日
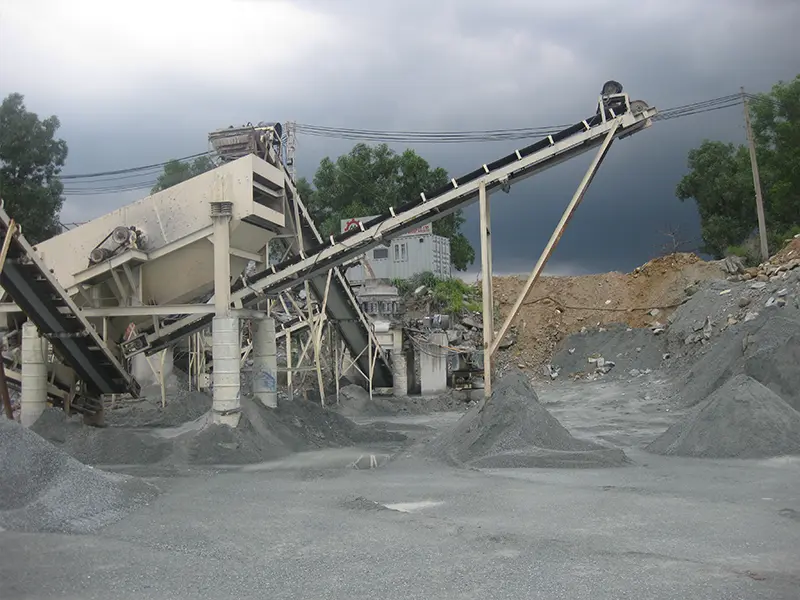
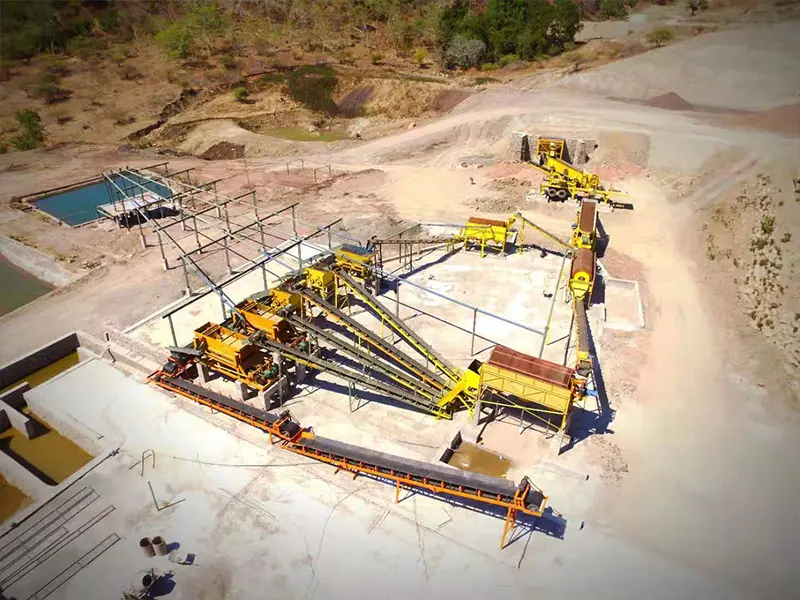
The Problem of Manufactured Sand Loss and Solutions
2025年5月13日Blog
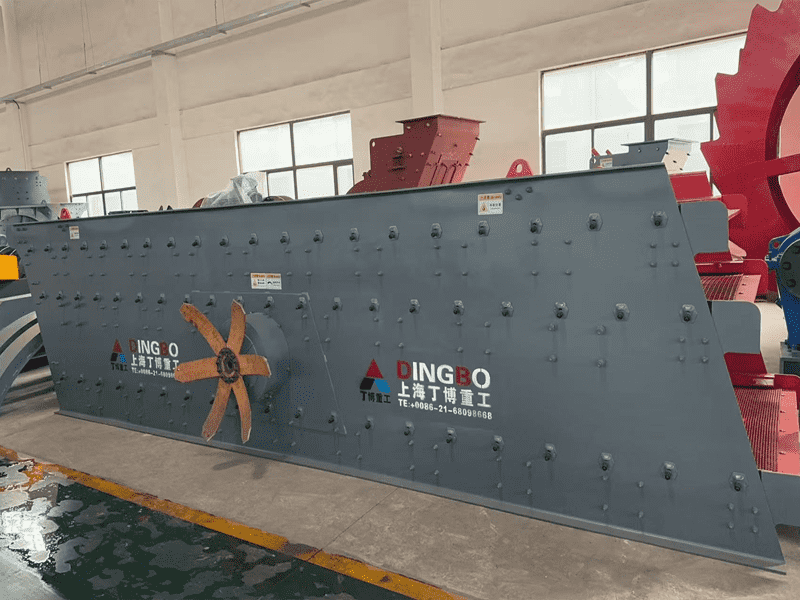
How to deal with bearing damage in a circular vibrating screen?
By applying the correct solution, the risk of bearing failure can be effectively reduced, extending the equipment’s lifespan. If you have questions regarding bearing selection or maintenance for circular vibrating screens, feel free to consult the engineering team at Dingbo Heavy Industry. We offer professional technical support and tailored solutions.
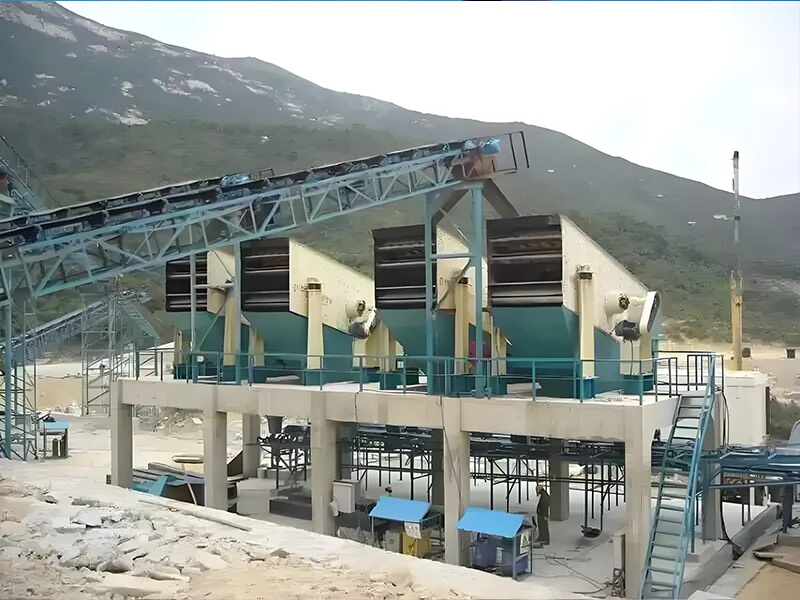

As a vital screening device, the circular vibrating screen is widely used in various production environments. However, bearing damage is a common issue during installation and operation. Engineers at Dingbo Heavy Industry have conducted in-depth studies on this problem and identified several potential causes of bearing failure, along with corresponding solutions:
- Improper Bearing Model Selection
Factors such as the bearing’s application category, maximum rotational speed, installation fit dimensions, clearance, and self-lubricating properties all influence its service life. If the wrong bearing model is selected initially, its lifespan will be significantly shortened.
Solution: Select a suitable bearing model. Commonly used bearings for circular vibrating screens include cylindrical roller bearings and spherical roller bearings, both of which offer high radial load capacity:
Cylindrical roller bearings can withstand higher rotational speeds and have strong load-bearing capacity for both dynamic and static loads but require high coaxiality in the bearing housing.
Spherical roller bearings have good self-aligning capabilities and can compensate for misalignment in the housing bore, but they cannot handle pure axial loads.
- Improper Fit Between Bearing and Housing Bore
The fit tolerance between the bearing and its housing bore is a critical factor during installation.
If the interference fit is too tight, it can deform the bearing raceway, causing abnormal vibrations during operation.
If the clearance fit is too loose, the bearing’s outer ring may slide relative to the housing, leading to a sharp temperature rise and eventual failure.
Solution: Choose proper fit tolerances. Ensure that the inner ring has a looser fit with the shaft, while the outer ring has a tighter fit with the housing bore.
- Improper Lubrication and Sealing Design
Currently, most vibration motor bearings use grease lubrication combined with a labyrinth seal, with typical seal gaps of 1–2 mm. However, during real-world operation, as bearing temperature rises, the grease viscosity decreases. At high spindle speeds, the lubricant tends to leak from the labyrinth cap, resulting in insufficient lubrication and eventual bearing damage.
Solution: Adopt thin oil lubrication, redesign lubrication channels, and improve sealing design. Many manufacturers now use circulating thin oil lubrication systems combined with labyrinth seals and other non-contact seal structures for better performance.
- Ignoring Shaft Thermal Expansion
During operation, vibration motor temperatures usually range from 35–60°C, and the thermal expansion of the shaft must not be overlooked.
Solution: Design one end of the bearing with a transitional or clearance fit, allowing the motor shaft to slide relative to the bearing’s inner ring during thermal expansion and contraction.
Recommend Equipment
Solutions
Company Case
Request a Quote